
|
User Guide | Multi-Server | Workspaces | Database |
KASM User Guide
How to Start Using KASM
If you’re on this document, you probably need a KASM server. Whether you have a school-issued chromebook or you want to try out KASM servers rather than directly downloading VS code and other tools onto your machine, this is the guide for you! If you are unfamilar with KASM Servers, check out this documentation first!
Now, we can move on to actually creating your KASM account. If you haven’t already, make an account on site. If you need a KASM server, make sure to click the checkbox next to KASM server needed.
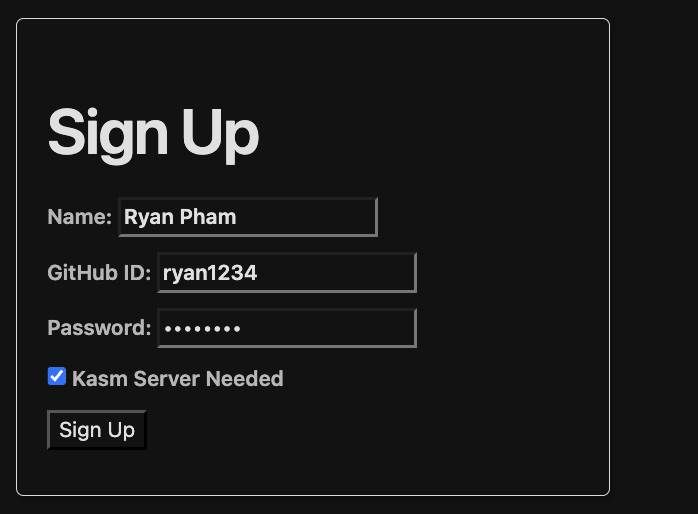
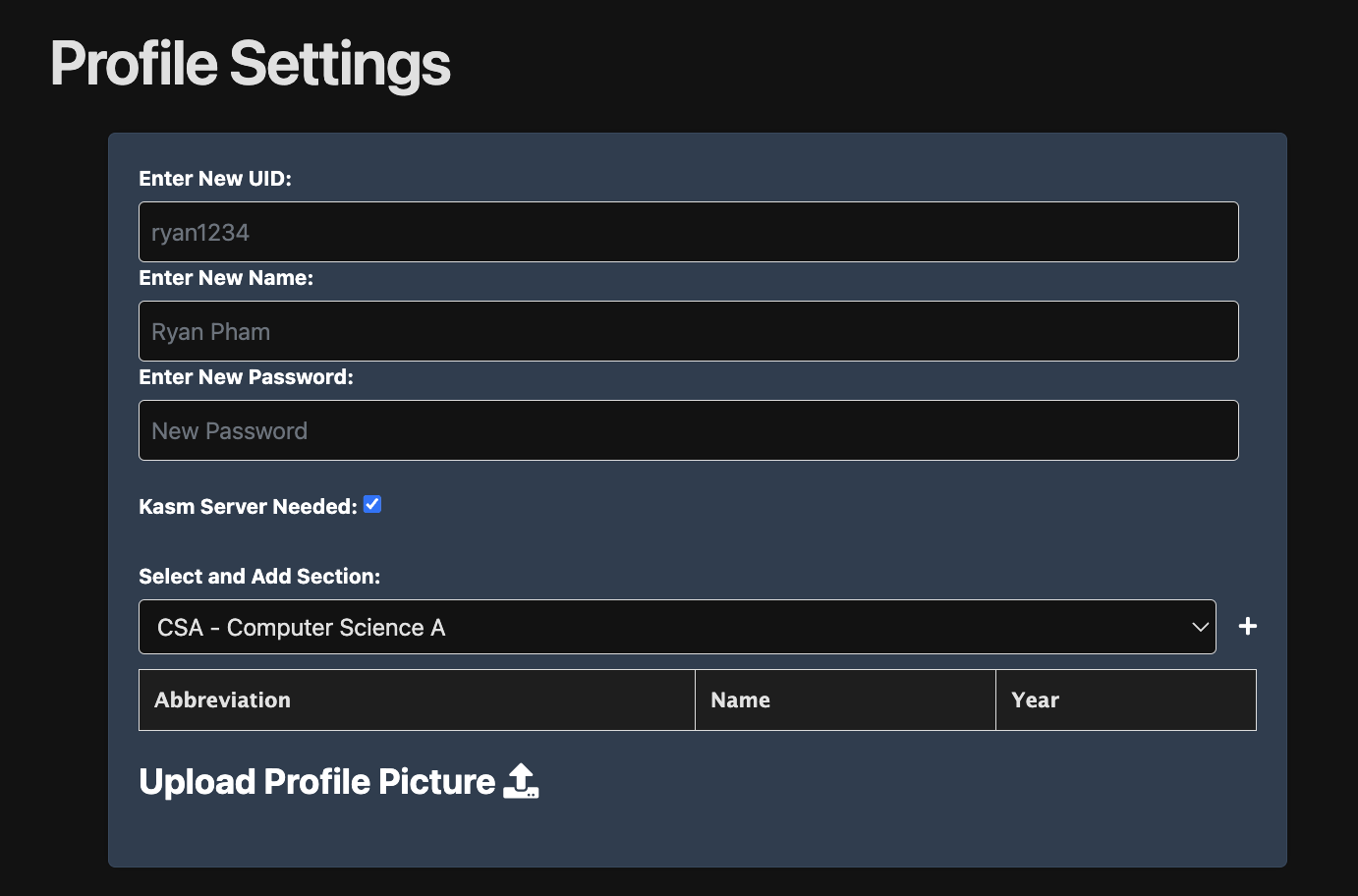
If you already made an account, log in and check your profile to see if you have KASM server needed. If you do, you have already been created as a KASM user. If not, click on the KASM user checkbox and an KASM user will be created based with the credentials you use to log in to ncs.org.
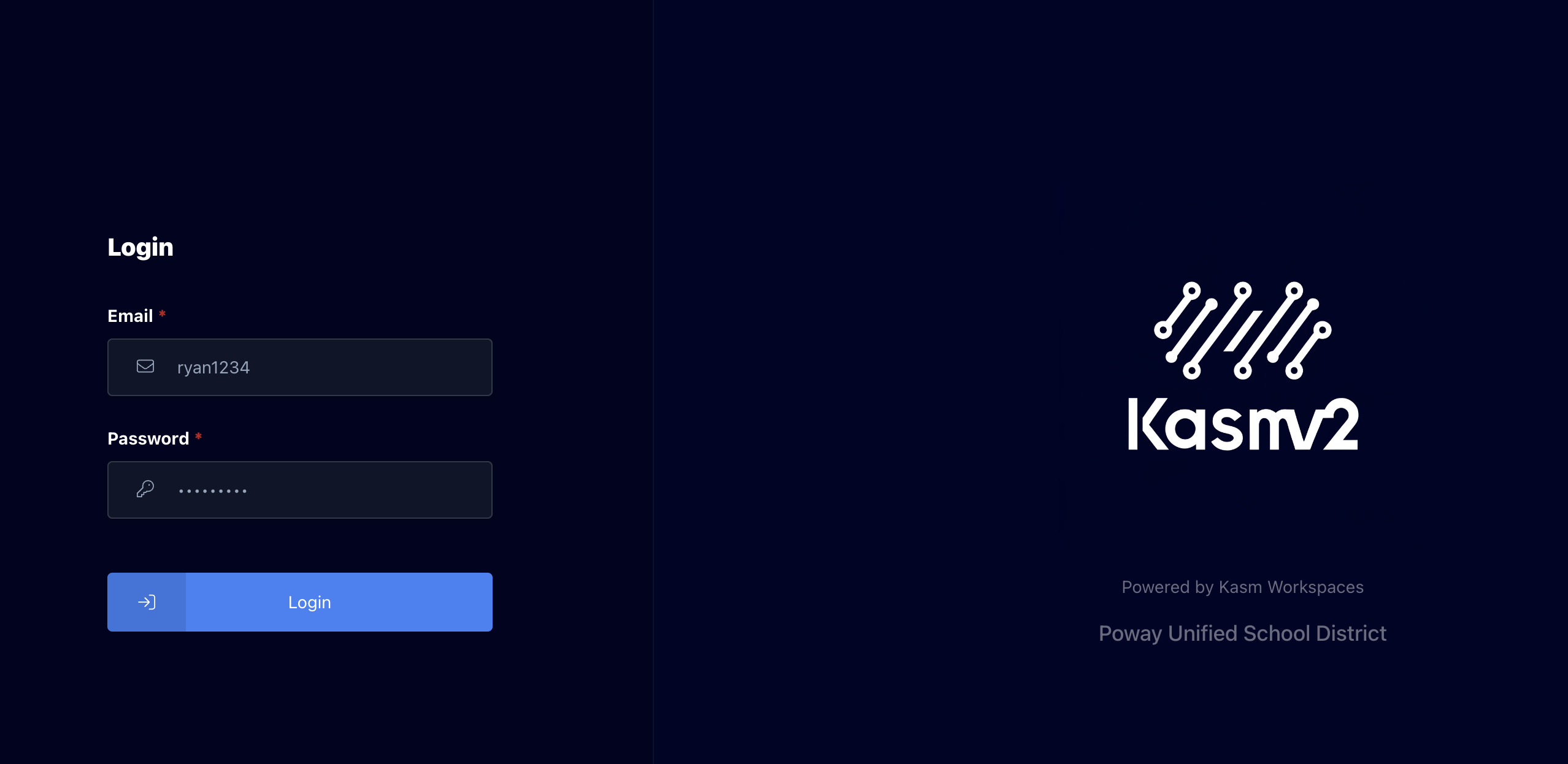
Then navigate to this site and use the same credentials you used to log in ncs.org in the login page.
Choose the the CSA workspace. If you are enrolled in CSA, CSP, or CSSE we will use the same workspace.
After you click on a workspace, you should see this screen:
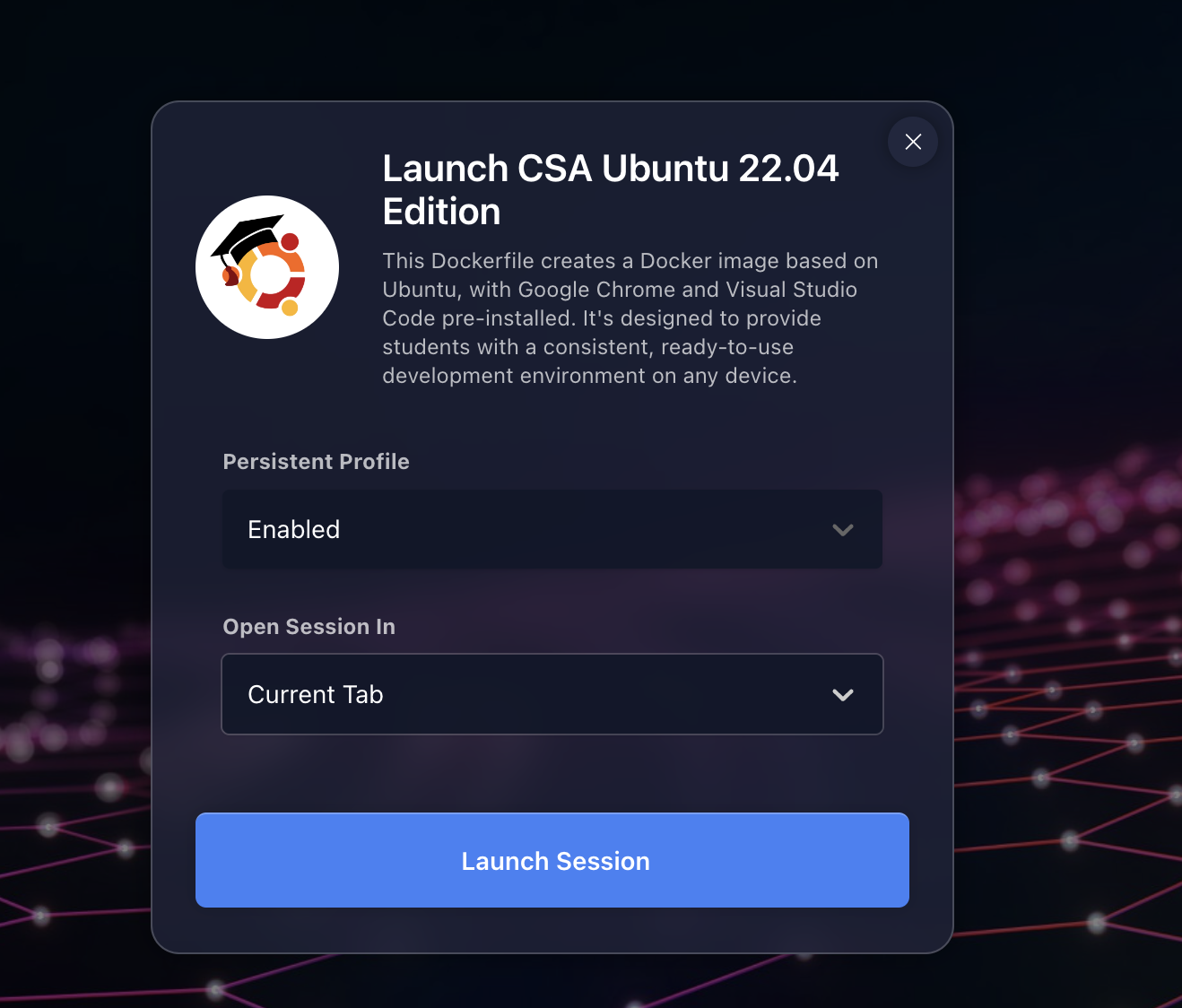
Once you launch the session, you should see this screen:
Then, you can click on the vscode icon to get here:
Project and Tool Setup
Now, we can set up the tools you need on VS Code.
Clone your repository
Click Application and open a Terminal Emulator. This opens a Terminal with a prompt default:~$. After the prompt we will type shell commands.
# Make a directory for your project
mkdir nighthawk
cd nighthawk
# Clone you personal repository, we wil use student_2025 in this example
git clone https://github.com/nighthawkcoders/student_2025.git
---
<br>
### Personalize your project
We need to edit a file and make changes according to your personal GitHub account.
#### Navigate using cd
Use the **cd** command to navigate to the directory containing the `activate.sh` file.
```bash
# Locate file in your cloned project
cd ~/nighthawk/student_2025/scripts
Open file with nano
nano activate.sh
Edit the Environment Variables
Use the arrow keys to navigate to the lines containing export GIT_USER_NAME and export GIT_USER_EMAIL.
Change jm1021 and jmort1021@gmail.com to your personal GitHub username and email.
export GIT_USER_NAME="your_github_username"
export GIT_USER_EMAIL="your_email@example.com"
Save the Changes
- Press
Ctrl+Oto save the changes. - Press
Enterto confirm the file name.
Exit nano
- Press
Ctrl+Xto exitnano.
Finish Tool Setup
After making the changes, you need to activate the environment to apply the new settings.
The script will take about 5 minutes to run.
# Move to Project Directory
cd ~/nighthawk/student_2025
# run activate script
./scripts/activate.sh
Version Checks
From here the steps should behave the same for all.
- Close existing terminal!!!
- Then start a new terminal. Start and stop are required to make sure changes to you machine have taken effect.
- Run each check below, if the check does not work, you will need to backup to resolve it now!!!
# Show the active Ruby version, it needs to be 3 or higher
ruby -v
# Bundler version, it is part of Ruby install
bundle -v
# Show active Python version, it needs to be 3.10 or better
python --version
# Show Jupyter packages, nbconvert needs to be in the list of installed
jupyter --version
Starting a Project
The following commands are the same for all machine types, terminals, and projects. The previous installation steps were to ensure all machine types had compatible tools.
Follow the steps in order.
-
Open a Linux-supported Terminal
- Move to your home directory:
cd cd nighthawk - Prepare project prior to opening VS Code:
# move to project directory cd student_2025 # activate virtual environment, observe prompt change after running it source venv/bin/activate # check if jupyter kernels are activated jupyter kernelspec list # if all worked well open VSCode code . - At this point or in near future, you may be asked to establish keychaing (KASM) and/or authenticate with GitHub. Follow the dialog and instructions. If keyring appears; be sure to authenticate. Using credentials similar to GitHub should be OK.
Open Project and Make
All students are building a GitHub Pages website. These steps get your website running each time you re-activate your desktop (local or cloud).
-
Open a terminal
-
Type
cd ~/nighthawk/portfolio/student_2025 -
Activate virtual environment
source venv/bin/activate -
Open VSCode
code . -
Open a VSCode Terminal
-
Type
makeThis runs a build to a local server. Repeat this command as often as you make changes. -
Hover then Cmd or Ctl Click on the Server address http://127.0.0.1 … provided in the terminal output from the make command.
### Congratulations!!! An output similar to below means tool and equipment success ###
johnmortensen@Johns-MBP portfolio_2025 % make
Stopping server...
Stopping logging process...
Starting server...
Server PID: 48190
Terminal logging starting, watching server...
Server started in 3 seconds
Configuration file: /Users/johnmortensen/vscode/portfolio_2025/_config.yml
To use retry middleware with Faraday v2.0+, install `faraday-retry` gem
Source: /Users/johnmortensen/vscode/portfolio_2025
Destination: /Users/johnmortensen/vscode/portfolio_2025/_site
Incremental build: disabled. Enable with --incremental
Generating...
Remote Theme: Using theme jekyll/minima
done in 2.493 seconds.
Auto-regeneration: enabled for '/Users/johnmortensen/vscode/portfolio_2025'
Server address: http://127.0.0.1:4100/portfolio_2025/
Make workflow (local build: make, make clean, make stop, make convert)
These commands are used to build and manage a localhost version of the website. The purpose of this is to verify and test code changes prior to pushing changes to GitHub Pages.
-
make: Runs the local server. -
make clean: Stops the local server and cleans the files. -
make stop: Stops the local server. This means you will be unable to access your blog on http://localhost until you runmakeagain. -
make convert: Converts Jupyter Notebook files. Run this if your.ipynbfiles are not updating on the server; it may assist in finding the error.
VSCode Commit and Sync Workflow
All students will be writing and changing code. These steps allow you to change the website, first locally and then on public location.
+-------------------+ +-------------------+ +-------------------+ +-------------------+
| | | | | | | |
| VS Code Editor | ----> | Local Git Repo | ----> | Remote GitHub | ----> | GitHub Pages |
| | | | | | | |
+-------------------+ +-------------------+ +-------------------+ +-------------------+
| | | |
| | | |
v v v v
Save Files Commit Changes Sync Changes Public Website
Local Website
Detailed Steps
- Save Files in VS Code:
- Edit your files.
- Save the changes (Cmd + S on Mac or Ctrl + S on Windows/Linux).
- Verify changes on desktop webserver.
- Commit Changes in VS Code:
- Click on the “Source Control” icon in the left sidebar.
- Stage your changes by clicking the plus sign next to the files.
- Enter a commit message.
- Click the “Commit” button.
- Sync Changes to GitHub:
- Click the “Sync Changes” button in the Source Control view.
- This pushes your local commits to the remote GitHub repository.
- Update GitHub Pages:
- GitHub Pages automatically rebuilds your site with the latest changes.
- Visit your public website at https://
.github.io/student_2025 to see the updates.